Patients are evaluated using a PET scanner after intravenoulsy injected with a radioisotope. This test is much faster than traditional myocardial stress test and can be completed within 30 minutes. It is also more accurate with the advantage of assessing individual coronary arteries and coronary flow reserve non invasively. All these make cardiac PET ideal for intermediate risk patients requiring risk stratification. This includes diabetics, stroke patients, renal impaired patients, patients with implants and post revascularisation patients (stents, CABG).
This uses ultrasonic energy that is directed over the chest wall to obtain images of the heart. These images show the heart's position, motion of the walls of the heart, the interior chambers, valves of the heart and blood flow within the chambers of the heart. This can help to determine if the heart valves are functioning properly or if there is an abnormal communication or flow between the chambers or the major blood vessels.
read more

Cardiac stress testing (ECG stress test) is used in the diagnosis of coronary heart disease and for risk stratification and monitoring of patients with known heart disease. In patients with coronary blockage, a blood supply that is adequate at rest, may not be adequate when there is an increased need for oxygen. Stress testing is less invasive and less expensive than cardiac catheterization, and it detects abnormalities of blood flow.
read moreCoronary Angiography (CTA) is a non-invasive heart imaging modality that produces high-resolution, 3-dimensional pictures of the heart and great vessels, to determine the presence of fatty or calcium deposits (plaques) in the coronary arteries. Coronary CTA is able to rule out significant narrowing of the major coronary arteries and detect "soft plaque," in the coronary artery walls that may lead to heart problems in the majority of individuals. The calcium-score screening is a test used to detect calcium deposits found in atherosclerotic plaque in the coronary arteries. It is used to evaluate the risk for future coronary artery disease.
Holter monitoring involves a portable device that enables continuous monitoring of the electrical activity of the heart or ECG. We can monitor heart rhythms for more than 2 weeks. This helps us to detect transient and short cardiac arrhythmias. In addition, it can monitor pacemakers, evaluate how well medications are working and assess the heart's electrical activity during episodes of chest pain.
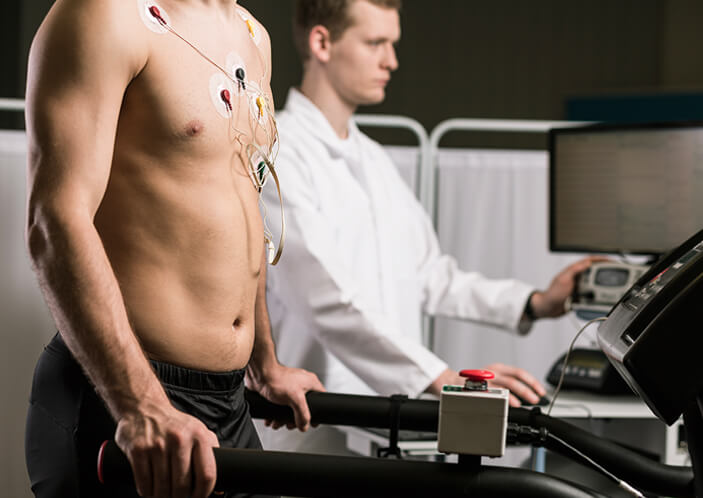
The treadmill exercise test is a test that measures the heart’s tolerance for exercise and helps to detect coronary heart disease. The treadmill stress test involves walking and /or running on a treadmill machine while recording the patient’s ECG and blood pressure throughout the test.

Holter monitoring involves a portable device that enables continuous monitoring of the electrical activity of the heart or ECG. We can monitor heart rhythms for more than 2 weeks. This helps us to detect transient and short cardiac arrhythmias. In addition, it can monitor pacemakers, evaluate how well medications are working and assess the heart's electrical activity during episodes of chest pain.
Blood tests are necessary for making accurate medical diagnosis. Our comprehensive range of blood tests include full blood count; lipid profile, kidney, liver and thyroid function tests; diabetes, bone, gout, Hepatitis B and cancer screening.
Hybrid PET CT involves the combination of Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Computed Tomography (CT) systems. The main advantage of hybrid PET CT is the visualisation of both coronary artery anatomy and understanding physiological significance during the same imaging session. Whereas coronary CT angiography provides information on the presence and extent of the stenosis in the coronary artery that leads to coronary artery disease (CAD), these new PET blood flow tracers provide information on the downstream functional significance of these obstructive lesions. Currently, the clinical applications mainly focus on the identification of coronary artery stenosis, which can be treated by coronary interventions. With advances in technology, CT angiography may allow imaging of the plaque morphology, not only going beyond the assessment of the luminal stenosis but also allowing the new radio-labelled ligands in the application of PET, to assess plaque biology and instability. This is particularly relevant in asymptomatic patients with coronary risk factors.
Invasive coronary angiography and intravascular physiological assessment involves a medical imaging technique that is used to visualize the inside of blood vessels. This is done by injecting a radio-opaque contrast agent into the blood vessel and imaging using X-ray based techniques such as fluoroscopy. Angioplasty (stenting) or percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) or Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) is widely used for the treatment of the blockages of the coronary arteries. Primary angioplasty is the mechanical reopening of an occluded vessel using a balloon-tipped catheter in patients with heart attack. The earlier primary coronary intervention is provided, the more effective it is.
read more
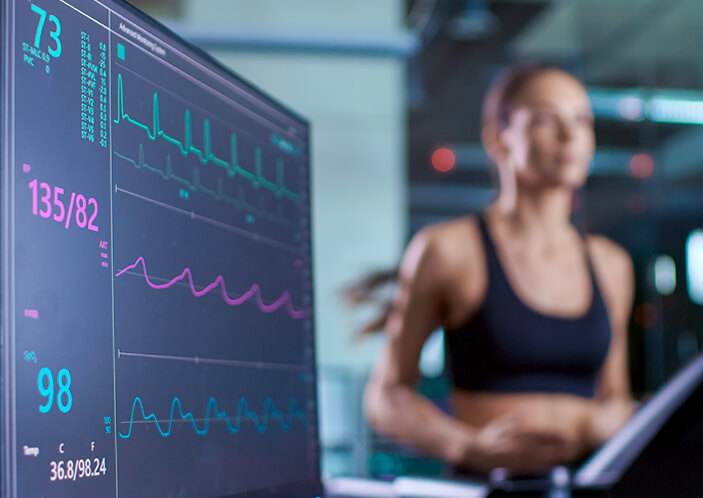

Besides general cardiac screening, we also have screening for athletes needing cardiac clearance and exercise prescription prior to their events. After exercise testing, the clinical information obtained is applied to achieve maximum exercise benefits for each individual patient.

We provide individualised treatment to both the sick and those who are apparently healthy but want to reduce their future risk of cardiovascular disease.
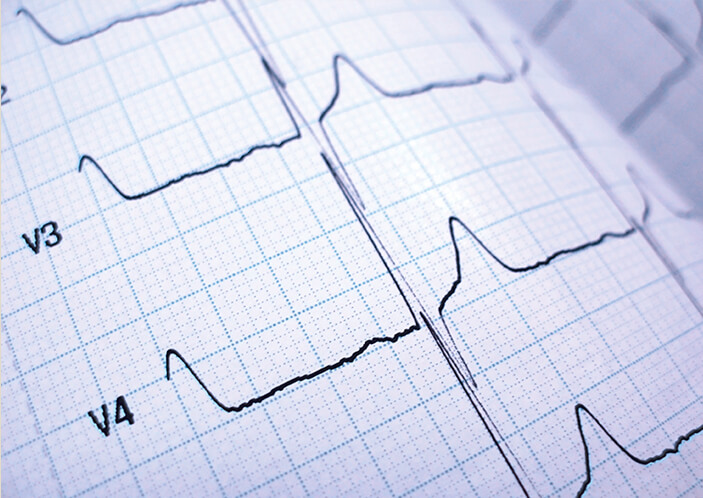
This is a test that captures the electrical activity of the heart, externally, at a point of time and is recorded by electrodes placed on the skin.
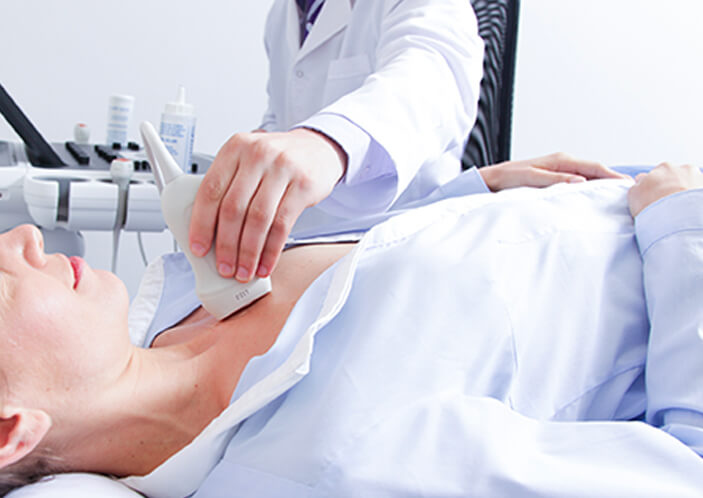
Carotid ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves to image the interiors of the two large arteries in the neck which supply the brain with oxygen-rich blood. Too much plaque in a carotid artery can cause a stroke