Transthoracic Echocardiogram
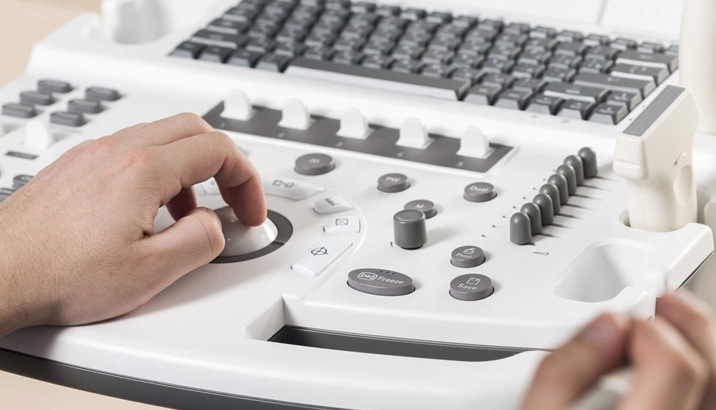
The most standard type, transthoracic echocardiogram, is non-invasive and works similarly to an X-ray and a regular ultrasound. In this method, a handheld transducer will be placed on your chest over the heart. A transducer is a device that transmits ultrasound waves to capture live images (sonograms) of the heart’s chambers and vessels, which can be viewed from a monitor. A transthoracic echocardiogram is done to check for structural heart defects and evaluate cardiac function and blood flow.
Transesophageal Echocardiogram
In cases where high-resolution images of a specific part of the heart are required, or if a transthoracic echocardiogram is unable to provide clear images of the heart’s structures, a transesophageal echocardiogram is recommended. It involves a thin, flexible tube equipped with a small transducer, which is inserted down the throat, and into the oesophagus behind the heart. This method gives more access to the heart and reduces sound wave interference from the lungs, ribs and chest.
Doppler Echocardiogram
The Doppler echocardiogram is done to measure and evaluate the amount, speed and direction of blood flow to the heart’s chambers and vessels. Performed alongside transthoracic or transesophageal echocardiograms, this method is used to detect abnormal blood flow and pressure indicative of issues in the heart’s valves or walls.
Stress Echocardiogram
Coronary artery problems can be detected and assessed through a stress echocardiogram. In this method, the patient undergoes a standard echocardiogram before and after exercising on a stationary bike or treadmill. This test helps the cardiologist determine the effects of stress on the heart, as well as the amount of stress that the heart can handle.